1Introduction
The construction of indoor environment plays a vital role in human comfort and health. People's attention to indoor environment is no longer limited to comfort, but also puts forward requirements for indoor air quality. A variety of air conditioning equipment and air supply forms also appear, MX fabric air distribution system is one of the new air supply system.
The MX fabric air distribution system uses fiber as the material, and uses the permeability of the fiber to supply air, and at the same time, different holes or slits can be opened on the distribution system to achieve jet or slits to supply air to meet the needs of different air flow organizations. Air flow organization has an important impact on indoor air environment and air quality, which is directly related to indoor temperature, regional flow rate and air conditioning energy consumption, and is an important part of air conditioning. If the indoor air flow organization is effectively predicted in the design stage of HVAC project, the best air conditioning scheme can be worked out. CFD(Computational Fluid Dynamic) is a rapidly developing computer aided design technology in recent years. The application of CFD technology in indoor air conditioning design can effectively simulate air flow organization before equipment installation, and predict the temperature field and velocity field of indoor air flow under various working conditions, so as to achieve optimal design scheme.
Based on the theories of computational fluid dynamics and heat transfer, this paper establishes physical models of traditional air supply system and slit air supply of fiber air distribution system on the basis of a specific closed room. The three-dimensional turbulent mathematical model of air flow in an indoor air-conditioned room is established through gambit, and FLUENT software is used. The airflow structure of traditional air supply system and fiber air distribution system is simulated respectively.
2 Model structure and parameters
2.1Geometry
According to the space size of a specific closed room, gambit software is used to build its structure model. The space size of the model room is X×Y×Z=6.8m×4.6m×3m. Where, X is the direction of room length, Y is the direction of room width, and Z is the direction of room height. Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2 show the geometric structure diagram of the traditional air supply model and the slit air supply model of the air distribution system respectively. As shown in Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2, the traditional air supply system adopts the air supply mode of up and down. The model has two air supply ports and two return air ports. The air distribution system adopts the slit air supply mode, which also adopts the upper air supply and the lower return air supply mode, and the air supply port is the 3 o 'clock and 9 o 'clock direction on both sides of the Y direction air distribution system.
In the traditional air supply model shown in Figure 2-1, the outlet size of the diffuser is 0.25m×0.25m, the diffuser is attached under the ceiling, and the thickness is 0.2m. The diffuser is located at X=2.3m in the width direction of the room, and X=-2m in the length direction of the room. The north diffuser is located at X=-2m, and the south diffuser is located at x =2m. The return air area of the return air outlet is 0.4m×0.2m, the thickness is 0.2m, and the height from the ground is 0.3m.
In the air distribution system supply model shown in Figure 2-2, the length of the air distribution system is 4m, the pipe diameter is 300mm, the air pipe elevation is 2.8m, and the slit width is 12mm. The air duct is located at Y=2.3m in the width direction of the room, the north end of the air duct is located at X=-2m, and the south end is located at X=2m. The size of the return air surface of the return air outlet is 0.4m×0.2m, the thickness is 0.2m, and the height from the ground is 0.3m.
Figure 2-3 and Figure 2-4 are the grids divided by the traditional air supply model and the slit air supply model of the air distribution system using gambit software respectively.
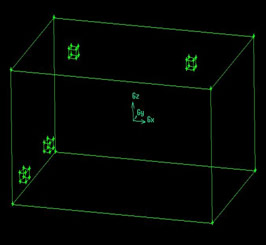
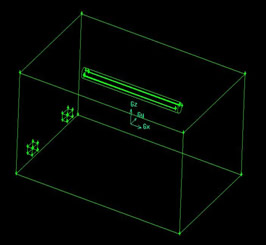
Figure 2-1 Traditional air supply model
Figure 2-2 Slit air supply model of the air distribution system
2.2Model calculation parameter
The indoor air temperature in summer is set at 25℃ (298K), the air supply temperature of the air conditioner is 18℃ (291K), and the indoor air humidity is 50%. Traditional air supply system in summer air supply outlet wind speed: 2m/s; Air distribution system slit outlet speed: 4m/s;
The load of this simulation experiment is borne by the enclosure structure of the room. The ceiling load is 10W/m2, the west wall and north wall load is 20W/m2, the east wall and south wall load is 10W/m2, and the floor load is 25W/m2. The wall temperature is set to 300K.
|
|
| Figure 2-3 Grid diagram of the traditional air supply model | Figure 2-4 Grid diagram of the air supply model of the air distribution system |
3 Simulation results and analysis
3.1 Simulation model specification
(1)As mentioned above, the model space is established under the spatial orientation of X, Y and Z. The X-axis is the direction of room length, Y is the direction of room width, and Z is the direction of room height.
(2)The working area mentioned in this simulation refers to the area with a confined space height of 0.5m-1.8m.
3.2 Simulation result analysis
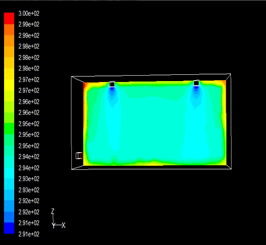
|
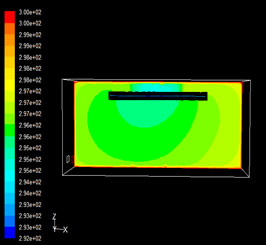
|
| Figure 3-1 Temperature distribution of conventional supply air (Y=0) | Figure 3-2 Supply air temperature distribution (Y=0) |
Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 show the temperature field of Y=0 section in the model under summer working conditions, which can observe the temperature distribution of the working plane in summer. In the traditional air supply model shown in Figure 3-1, we find that the temperature of the roof is higher, with 30 ° C, and the temperature value decreases with the decrease of height. At the same time, in the vertical lower part of the diffuser tuyere, there can be observed a cold zone, its temperature is lower than other areas, there is a large temperature gradient; However, we observe the slit air supply model of the air distribution system as shown in Figure 3-2, and its temperature field basically does not change in the height direction. This fully shows that the temperature field of the traditional air supply system is stratified in the height direction, and the vertical temperature difference is large, and there is a phenomenon of cold air falling, while the slit air supply model of the air distribution system has no obvious vertical temperature difference, and can effectively improve this phenomenon of cold air falling.
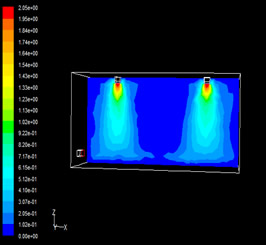
|
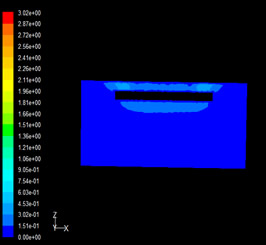
|
| Figure 3-3 Distribution of traditional supply air velocity (Y=0) | Figure 3-4 Distribution of air supply velocity of the air distributor (Y=0) |
As can be seen from Figure 3-3 and Figure 3-4, there are two obvious high-speed areas in the velocity field of the traditional air supply model in the height section, with a speed of up to 1m/s, which is caused by the concentrated injection of the air supply system with a large flow through the diffuser, which will make people feel the sense of blowing in the room. There will be a sense of blowing, especially in the place near the air jet area, the sense of blowing is obvious; Air distribution system slot air supply, in the slot out of the air jet area, there will be a certain degree of blowing sense, but in the working area, the sense of blowing will be reduced, according to this point, we can consider adjusting the air distribution system installation height and slot tuyere opening direction to achieve the working area without blowing sense. According to relevant studies, when the cooling load of the ground is as high as 300W/m2, the air supply without obvious blowing sensation can be achieved.
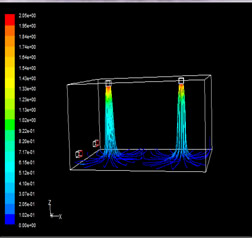
|
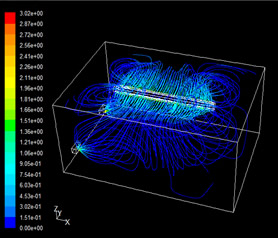
|
| Figure 3-5 Flow line of the traditional air supply mode | Figure 3-6 Flow line of the air distribution mode |
As can be seen from Figure 3-5 and 3-5, when the air distribution system is supplying air, the air outlet jet speed is large and the attenuation is fast, which will produce the induced air supply effect. This effect can accelerate the mixing speed between air streams in the room, and also increase the mixing of air streams, so that the indoor flow field (including temperature field and velocity field) is more uniform. The uniform air supply effect can avoid the feeling of blowing due to too much air supply in some areas or the air supply is too small and the air quality is poor, and it will cause an increase in ventilation energy consumption.
4 Conclusion
By using CFD method to compare the traditional air supply mode with the new air supply system MX air distribution system, it is found that the overall air supply of MX air distribution system can make the indoor air uniform, the temperature gradient is small, and better meet the comfort requirements. With the increasing demand for thermal comfort, the HVAC market urgently needs new HVAC equipment to improve the thermal comfort of the environment. As a new type of air supply system, MX air distribution system can not only achieve uniform air supply height, but also remove harmful volatile gases such as formaldehyde in the air. It is believed that Farui air distributor will gradually enter the field of vision of HVAC engineers and be widely used in various fields.
