1, the basic principle of air supply mode
Indoor air quality not only affects people's comfort, but also has a certain impact on the work efficiency of personnel. The traditional roof air supply belongs to mixed ventilation. The treated low temperature air is mixed with indoor air through the roof air supply diffuser to eliminate indoor residual heat and humidity, and indoor temperature and humidity are evenly distributed in space. However, the indoor air quality of the roof air supply is poor, the energy consumption is high, and the use is also limited. The following describes the basic principles of floor air supply, station air supply and displacement ventilation.
1.1 Floor air supply

Floor air supply is another form of mixed ventilation, the treated air passes through the plenum under the floor, is sent into the room by the air supply diffuser, and is mixed with the indoor air. It is characterized by clean air from the bottom up through the personnel activity area, eliminate residual heat and humidity, and discharge from the exhaust outlet at the top of the room, and the indoor temperature is uniform. Due to the limited height of floor lifting, the amount of air supply is limited, and the floor air supply is mostly used in air-water systems.
1.2 Station air supply

Station air supply is a personalized air supply method that integrates regional ventilation equipment ventilation and personnel self-regulation. The air outlet is installed in the core area (human breathing area), connected to the air supply device under the floor through a hose, and the location of the air outlet can be flexibly changed according to the indoor facilities. Individuals can adjust the flow rate, velocity, direction and temperature of the air supply according to comfort needs. General floor air supply devices are installed in the surrounding areas (conference halls, lounges, walkways, etc.) to control the heat and humidity load of the indoor environment. Because modern office buildings are mostly designed in a unified style, the individual's demand for cold and hot air around them is quite different, and it is more suitable to install station air supply.
1.3 Displacement ventilation
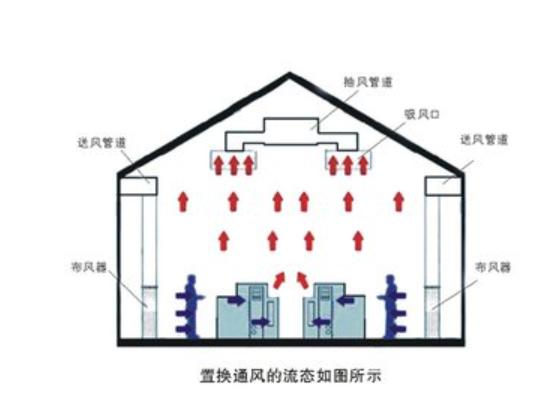
Displacement ventilation is a kind of downward air supply. The air flow is sent into the room from the diffuser located at the lower part of the side wall at a low speed, and rises to the working area under the action of floating lift, absorbing personnel and equipment loads to form a hot plume. In the process of rising, the hot plume continues to suck the surrounding air, and the flow rate gradually increases. Thermal stratification height divides the whole space into upper and lower zones, and the air in the lower zone presents a one-way "piston flow" from bottom to up, forming an obvious temperature gradient and pollutant concentration gradient along the height direction. The air in the upper area circulates, the concentration of pollutants is large, and the temperature tends to be uniform. At present, displacement ventilation is more used for air conditioning systems with a height greater than 2.4m and indoor cooling load less than 40W/m2. Displacement ventilation and floor air supply are both bottom-up and back forms, but there are differences between the two.
There are great differences in the indoor air flow organization of the above three air supply modes, and the air exchange efficiency of the three is greater than that of the roof air supply, and the energy utilization coefficient is large.
